 Occasionally, root canal treatment proves unsuccessful at resolving an infection in the tissues near a tooth’s roots. That’s when a minor surgical procedure called an apicoectomy may be recommended. Because this procedure is often performed with the aid of a microscope and other small specialized tools, it’s considered a type of endodontic microsurgery. Probably the most common type of root canal surgery, an apicoectomy involves removing a small portion of the apex (tip) of the tooth’s root, along with any surrounding hard or soft tissue that may be infected.
Occasionally, root canal treatment proves unsuccessful at resolving an infection in the tissues near a tooth’s roots. That’s when a minor surgical procedure called an apicoectomy may be recommended. Because this procedure is often performed with the aid of a microscope and other small specialized tools, it’s considered a type of endodontic microsurgery. Probably the most common type of root canal surgery, an apicoectomy involves removing a small portion of the apex (tip) of the tooth’s root, along with any surrounding hard or soft tissue that may be infected.
What would cause you to need an apicoectomy? There could be several reasons, including a canal that is blocked or inaccessible, an anatomical irregularity, or a fracture or crack in the tooth’s roots. The procedure is normally only recommended after one or more root canal treatments have been attempted, and have failed. Since this type of problem generally occurs near the apex of the root, the procedure is often an effective way to treat a persistent infection.
Before an apicoectomy procedure, diagnostic images (such as X-rays) of the affected tooth and surrounding bone, a careful review of your medical history including medications you take (both prescription and non-prescription), and other factors are reviewed. If an apicoectomy is recommended, the reasons for it will be explained to you.
The Apicoectomy Procedure
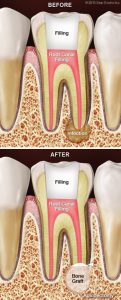
Root canal surgery is usually performed under local anesthesia such as a numbing shot, so you won’t feel any pain. To begin the procedure, a small incision is made in the gum, and the infection at the end of the tooth’s roots is exposed. The infected tissue is then removed, along with a few millimeters of the root tip itself. A dye may be used to help make cracks or fractures easy to see; if we discover that the tooth is fractured, it may be better to extract (remove) it at this time instead of completing the apicoectomy.
Next, a microscope and light are used to examine the tiny canals. They will be cleaned with an ultrasonic instrument, then filled with an inert material and sealed up with a small filling. To finish the procedure, a small bone graft may be placed at the affected site, and then the gum tissue covering the tooth’s root will be sutured (sewn) closed. X-rays may also be taken as the procedure nears completion. Afterwards, instructions on postoperative care will be given, and you’ll go home. Most apicoectomies take about 30 to 90 minutes to complete.
Following the procedure, you may experience some swelling and soreness in the area that was treated. Over-the-counter non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications (such as ibuprofen) are usually all that’s needed to control any discomfort. You can probably return to normal activities the following day, but you may want to avoid eating hard or crunchy foods or brushing vigorously for a few days afterwards. If your sutures aren’t self-dissolving, you will be asked to return in about a week to have them removed.
The Goal: Saving Your Tooth
Although apicoectomy is typically a safe and effective procedure, there are slight risks with any type of minor surgery. That’s why apicoectomies are not recommended unless further root canal treatment won’t be effective. An alternative treatment in most cases would be extraction of the tooth. However, our goal as dentists is to help you preserve your natural teeth for as long as possible.
While there are excellent methods of tooth replacement (such as dental implants), these involve further and more complex treatments, and they can be costly. An apicoectomy is generally a permanent and cost-effective solution which can help the tooth last for the rest of your life.